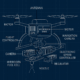
Permaculture
Permaculture is a word not too many know today but describes the future of food production for intelligent souls who want the best quality of life and body functionality available.
The agricultural sister of The Nutritional Diversity diet, permaculture studies how plants grow together as a sustainable, all-natural ecology. While several organic methods exist today, it is the permaculture method that is closest to nature and that will produce the high diversity needed for the diet’s minimum requirements.
Introduction to Permaculture as a Solution
Permaculture, a term coined from “permanent agriculture,” [Bill Mullison] is an innovative framework for creating sustainable ways of living and developing self-sufficient agricultural systems. It is based on the principles of working with, rather than against, nature; of thoughtful observation rather than thoughtless labor; and of looking at systems in all their functions, rather than asking only one yield of them.
Core Principles of Permaculture:
1. Earth Care: Priority is given to the health of natural systems and landscapes.
2. People Care: It seeks to support and help people to access resources necessary for their existence.
3. Fair Share: Encourages equitable distribution of resources and limits consumption to ensure sustainability.
How Permaculture Addresses Food Crisis and Climate Change:
1. Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Permaculture promotes diversifying crops, integrating animals into farming systems, and using renewable resources. This leads to healthier soil and ecosystems, which are more resilient to climate change and can provide a stable food supply.
2. Water Conservation: Permaculture designs include water harvest
 ng and efficient usage techniques, reducing water waste, and preserving this vital resource in agriculture.
ng and efficient usage techniques, reducing water waste, and preserving this vital resource in agriculture.
3. Carbon Sequestration: By increasing biodiversity and promoting the growth of a wide range of plants, permaculture systems can capture more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping mitigate climate change.
4. Reducing Chemical Use: Permaculture encourages organic farming, which avoids the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, reducing pollution and helping to maintain healthy ecosystems.
5. Soil Health: The emphasis on organic matter and biodiversity in permaculture helps build robust soil that can store more water and nutrients, making agriculture more resilient to both droughts and floods, common issues exacerbated by climate change.
6. Local Food Systems: Permaculture supports local food systems that reduce the carbon footprint associated with the transportation of food items and promote food security.
7. Resilience to Extreme Weather: By designing systems that are resilient and adaptable, permaculture can help communities withstand and recover from extreme weather events.
8. Education and Community Involvement: Permaculture is not just about agriculture; it’s also about community building and education. Teaching these practices helps spread sustainable methods and fosters community resilience.
Potential at Large Scale:
If applied on a large scale, permaculture has the potential to significantly mitigate the food crisis and combat climate change. By transforming large agricultural systems to follow permaculture principles, there could be a dramatic shift towards sustainability. This includes large-scale rehabilitation of degraded land, creating sustainable food systems in urban areas, and influencing policy to support sustainable agricultural practices.
The challenge lies in scaling up these practices while maintaining their core ethical principles. This would require a paradigm shift in how societies view agriculture, the environment, and their interdependence, along with substantial support from governments, organizations, and communities. However, the long-term benefits for the planet and future generations make this challenge worth tackling.
- *Best Investment.
- Guerilla Permaculture – The Truly Free System!
Permaculture Importance Explained
This video was made for a permaculture for kids education pilot.
Permaculture is the new term for the study of, alternative organic farming that grows many foods together.. just like how plants grow and live all over each other in the wild. It is the natural opposite of mono-culture farming, which is one thing grown over and over again in a high-production system known as modern agriculture.
This modern agriculture system is dependent on modern agricultural chemicals, and large machines to administer them and harvest the crops for mass distribution. Because this one crop planted over and over to consume a large piece of land is not in balance with nature and is not supportive of other life forms, other than the one crop; the insecticides and chemical nutrients must replace or support aspects of life for the crop it is not receiving from a natural environment. This practice for profit, produces lower-grade foods, that may appear nicer in the store, but is far less quality than a permaculture-grown food, and could even be linked to disease and sickness. Ultimately modern agriculture today is a chemically dependent farming model that actually kills the earth it is farmed on.
Beyond this there are tiered products for heavily damaged soil that is completely missing nutrients; from this dead earth, to replace normal life cycles with concentrated super chemical foods that enable high production in dead earth! The dry, crusty life-cycle-less soil will eventually become so damaged it won’t be usable for any purpose at all, like the Sahara. Crop rotations and less obtrusive, more earth-conservative intended practices have formed of late, but in this case; a permaculturist would argue that the entire mono-crop idea needs to be put away, something that would make all the tractor companies and ‘Agricultural Supply’ people lose money, and Universities would have to throw out the textbooks and get new teachers. A Permaculturist may go on to say we have made a toxic food mess in pursuit of profit and the central distribution/grocery store food markets.
 The word Permaculture comes from the two words, permanent and culture, and means to represent self-sustaining, low-maintenance, totally organic culture. This is a study often of God’s way of nature; a cycle of life containing billions of separate organisms working together in a constant flow and cycle of life and liberation. The forests and jungles are successful permaculture, and the modern plant lover finds joy in trying to design his own. It is to me the most interesting art form, of mastery, to be a Permaculture Designer and paint in biology. The study is in many respects the sister science to Nutritional Diversity Science.
The word Permaculture comes from the two words, permanent and culture, and means to represent self-sustaining, low-maintenance, totally organic culture. This is a study often of God’s way of nature; a cycle of life containing billions of separate organisms working together in a constant flow and cycle of life and liberation. The forests and jungles are successful permaculture, and the modern plant lover finds joy in trying to design his own. It is to me the most interesting art form, of mastery, to be a Permaculture Designer and paint in biology. The study is in many respects the sister science to Nutritional Diversity Science.
‘Permaculture‘ is the most applicable search term on the net now regarding what your Nutritional Diversity should come from. The subject of permaculture really has some endless depth so we will brush very lightly over a very profound idea at this website.
Permaculture is talking about an opposition to mono-culture which is what modern agriculture remains to be as senseless as it is. Monoculture is the same thing grown next to the same thing for miles. It ruins the soil and justifies harsh chemical pesticides and fertilizers. Its what you can send your kids to learn at a major University for hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Permaculture is trying to take from God’s page a bit, like the Forrest and the jungles are where many different plant species facilitate the cycle of life on earth. How we ever arrived at monoculture farming I will never know and probably a devil does.
A permaculture builds soil rather than destroys it. It attracts and promotes a balanced life rather than festering unbalanced sickness and survival. It’s the answer to the food crisis and the re-stabilization of the planet. We humans are biologically dependent on the Permacultures of the world (mostly God’s).
For those seriously interested in the science of Permaculture, the Complete Designers Guide, the essential Bible for permaculturists such as myself written by one of the Fathers of observation Bill Mullison. He also offers an Introduction to Permaculture.
and Beyond…
Bio-dynamic farming a system of Permaculture written by Rudolph Steiner in 1920, is the foremost and proven best nutrition cultivation method used on the planet today.
This is the ultimate form of written Permaculture, of course, each culture will be a fingerprint, a one-of-a-kind individual body reflective of the farmer.
Espanol
La permacultura, un término derivado de “agricultura permanente”, es un marco innovador para crear formas de vida sostenibles y desarrollar sistemas agrícolas autosuficientes. Se basa en los principios de trabajar con la naturaleza, en lugar de en contra de ella; de observar cuidadosamente en lugar de trabajar sin pensar; y de ver los sistemas en todas sus funciones, en lugar de pedirles un solo rendimiento.
Principios Básicos de la Permacultura:
1. Cuidado de la Tierra: Se da prioridad a la salud de los sistemas naturales y paisajes.
2. Cuidado de las Personas: Busca apoyar y ayudar a las personas para que accedan a los recursos necesarios para su existencia.
3. Participación Justa: Fomenta la distribución equitativa de recursos y limita el consumo para asegurar la sostenibilidad.
Cómo la Permacultura Aborda la Crisis Alimentaria y el Cambio Climático:
1. Prácticas de Agricultura Sostenible: La permacultura promueve la diversificación de cultivos, la integración de animales en los sistemas agrícolas y el uso de recursos renovables. Esto conduce a suelos y ecosistemas más saludables, que son más resilientes al cambio climático y pueden proporcionar un suministro de alimentos estable.
2. Conservación del Agua: Los diseños de permacultura incluyen técnicas de captación y uso eficiente del agua, reduciendo el desperdicio de agua y preservando este recurso vital en la agricultura.
3. Secuestro de Carbono: Al aumentar la biodiversidad y promover el crecimiento de una amplia gama de plantas, los sistemas de permacultura pueden capturar más dióxido de carbono de la atmósfera, ayudando a mitigar el cambio climático.
4. Reducción del Uso de Químicos: La permacultura fomenta la agricultura orgánica, que evita el uso de fertilizantes y pesticidas sintéticos, reduciendo la contaminación y ayudando a mantener ecosistemas saludables.
5. Salud del Suelo: El énfasis en la materia orgánica y la biodiversidad en la permacultura ayuda a construir un suelo robusto que puede almacenar más agua y nutrientes, haciendo la agricultura más resiliente tanto a sequías como a inundaciones, problemas comunes exacerbados por el cambio climático.
6. Sistemas Alimentarios Locale: La permacultura apoya los sistemas alimentarios locales que reducen la huella de carbono asociada con el transporte de alimentos y promueven la seguridad alimentaria.
7. Resiliencia ante el Clima Extremo: Al diseñar sistemas que son resilientes y adaptables, la permacultura puede ayudar a las comunidades a resistir y recuperarse de eventos climáticos extremos.
8. Educación y Participación Comunitaria: La permacultura no se trata solo de agricultura; también es sobre construcción comunitaria y educación. Enseñar estas prácticas ayuda a difundir métodos sostenibles y fomenta la resiliencia comunitaria.
Potencial a Gran Escala:
Si se aplica a gran escala, la permacultura tiene el potencial de mitigar significativamente la crisis alimentaria y combatir el cambio climático. Transformando grandes sistemas agrícolas para seguir los principios de la permacultura, podría haber un cambio dramático hacia la sostenibilidad. Esto incluye la rehabilitación a gran escala de tierras degradadas, la creación de sistemas alimentarios sostenibles en áreas urbanas e influir en políticas para apoyar prácticas agrícolas sostenibles.
El desafío radica en escalar estas prácticas manteniendo sus principios éticos centrales. Esto requeriría un cambio de paradigma en cómo las sociedades ven la agricultura, el medio ambiente y su interdependencia, junto con un apoyo sustancial de gobiernos, organizaciones y comunidades. Sin embargo, los beneficios a largo plazo para el planeta y las generaciones futuras hacen que este desafío valga la pena enfrentar.